How to operate a drone opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety procedures to advanced flight techniques and legal considerations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, camera settings, and maintenance, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the skies and capture stunning visuals.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of technical understanding and responsible practice; this guide aims to provide both.
We’ll delve into the specifics of different flight modes, troubleshooting common issues, and adhering to relevant regulations. Whether you’re a beginner taking your first flight or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, this resource will serve as a valuable companion on your journey into the fascinating realm of drone technology. Prepare to take flight!
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is paramount for ensuring both the safety of the drone and those in its vicinity. Neglecting this crucial step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and potential legal repercussions. A comprehensive checklist ensures all systems are functioning correctly, minimizing the risk of unforeseen problems mid-flight.
Pre-Flight Inspection Importance
Pre-flight inspections are crucial for identifying potential issues before they escalate into problems during flight. This preventative approach minimizes the risk of accidents, protects your investment in the drone, and ensures compliance with safety regulations. A damaged propeller, for example, discovered before takeoff, prevents a potentially hazardous mid-flight failure.
Comprehensive Pre-Flight Checklist
A detailed pre-flight checklist should include:
- Battery Level Check: Verify that the drone battery is sufficiently charged and in good working condition. Check for any signs of damage or swelling.
- Propeller Inspection: Carefully examine each propeller for cracks, chips, or any signs of damage. Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- GPS Signal Strength Verification: Ensure the drone has a strong GPS signal before takeoff. A weak signal can lead to inaccurate positioning and control issues.
- Gimbal Calibration: Verify that the gimbal is properly calibrated and functioning smoothly. This ensures stable and clear camera footage.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire drone for any visible damage, loose parts, or obstructions.
- Flight Controller Check: Confirm that the flight controller is responding correctly and that all systems are communicating properly.
- Communication Range Test: Perform a brief test to ensure clear communication between the drone and the remote controller.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedure
A standardized takeoff and landing procedure enhances safety and minimizes the risk of accidents. This should be practiced regularly to build muscle memory and confidence.
- Clear the Area: Ensure the area is free of obstacles and people before initiating takeoff.
- Level Ground: Select a level and stable surface for takeoff and landing.
- Arm the Motors: Arm the drone motors according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Controlled Ascent: Initiate a slow and controlled ascent, maintaining visual contact with the drone at all times.
- Controlled Descent: For landing, initiate a slow and controlled descent, maintaining visual contact.
- Disarm Motors: After landing, disarm the motors immediately.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting, How to operate a drone
| Malfunction | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, power switch issue | Charge battery, try a different battery, check power switch | Check connections and wiring. |
| GPS signal lost | Weak signal, interference, obstructed view of satellites | Move to an open area, check for obstructions | Ensure GPS is enabled. |
| Motor failure | Motor damage, loose connections, ESC malfunction | Inspect motor, check connections, replace faulty components | Consult the manual for specific troubleshooting steps. |
| Unstable flight | Calibration issues, wind conditions, low battery | Calibrate sensors, fly in calmer conditions, check battery | Adjust flight settings as needed. |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and effective operation. Understanding the functions of the control sticks and various flight modes allows for precise maneuvering and creative aerial shots.
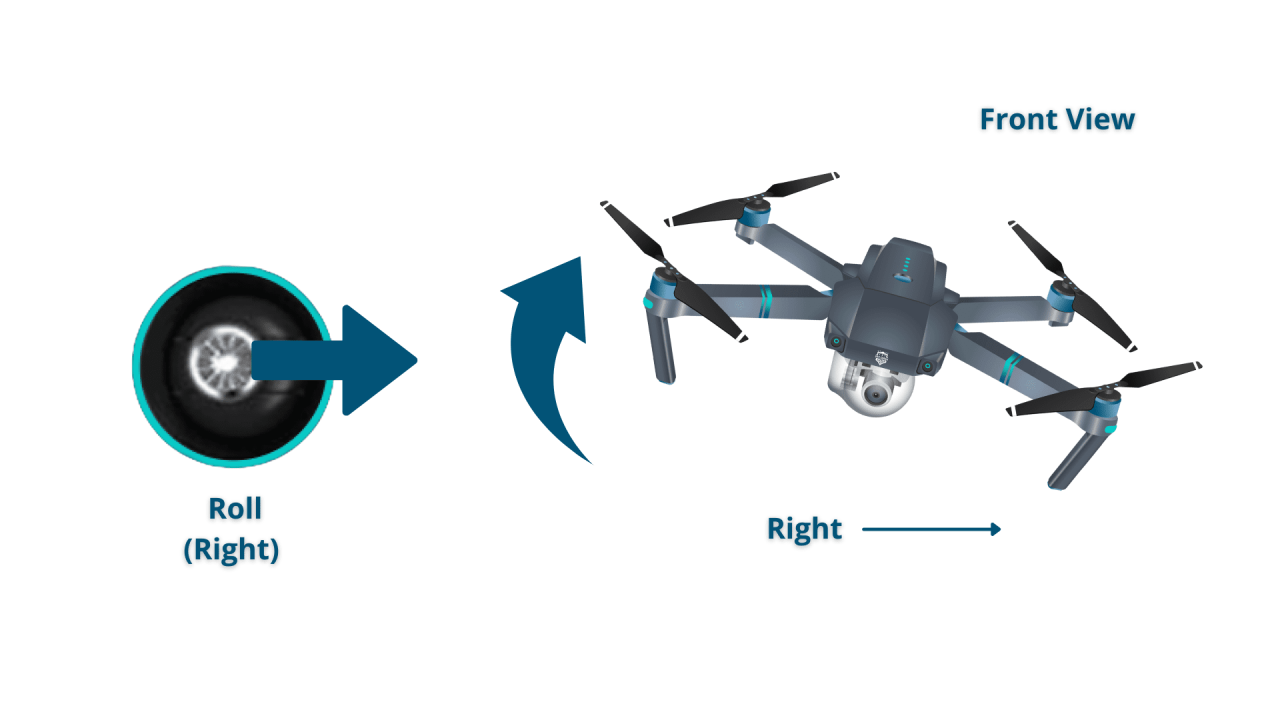
Drone Controller Functions
Standard drone controllers typically feature two joysticks. The left stick usually controls the drone’s altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls the drone’s forward/backward and left/right movement. Different drones might have slight variations, so consult your drone’s manual for precise details.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and a solid understanding of the controls; for a comprehensive guide, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Safe and responsible drone operation is crucial for both personal safety and respecting others’ airspace.
Flight Modes

Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Understanding their functionalities is crucial for adapting to diverse flight conditions and achieving desired camera movements.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a constant altitude, simplifying control and allowing for more precise camera movements.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS signals for positioning and stabilization, enhancing stability, especially in windy conditions.
- Beginner Mode: Limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, ideal for new pilots.
- Sport Mode: Offers increased speed and responsiveness for experienced pilots.
Drone Control Interfaces
Different control interfaces offer unique advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right interface depends on personal preference and flight requirements.
- Standard Controller: Offers precise control and familiar joystick interface, but can be bulky.
- Smartphone App: Convenient and portable, but may lack the precision of a dedicated controller.
Navigating a Simple Obstacle Course
Practicing navigation through a simple obstacle course helps develop piloting skills and improves spatial awareness.
- Plan the Route: Plan a safe and straightforward route through the obstacles.
- Start Slow: Begin with slow, deliberate movements to maintain control.
- Use Flight Modes: Utilize altitude hold and GPS mode for stability.
- Adjust Speed: Gradually increase speed as confidence and skill improve.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to improving navigation skills.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography
The camera is a key feature of most drones, enabling stunning aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and employing effective techniques significantly enhances image quality and creative possibilities.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Understanding aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for controlling the exposure and overall look of your images and videos.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera lens, affecting depth of field.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the length of time the camera’s sensor is exposed to light, impacting motion blur.
- ISO: Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light, influencing image noise.
High-Quality Aerial Photography and Videography
Achieving high-quality aerial media involves a combination of proper camera settings, stable flight, and creative composition.
- Use proper lighting: Avoid harsh midday sun; golden hour provides softer, more appealing light.
- Stable flight: Utilize flight modes like altitude hold and GPS mode to minimize vibrations.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds for visually appealing shots.
Smooth and Stable Footage
Smooth and stable footage is essential for professional-looking results. Different flight modes and techniques contribute to achieving this.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a consistent altitude, reducing vertical movement.
- GPS Mode: Provides stability in windy conditions.
- Smooth Movements: Avoid jerky movements; use slow, deliberate controls.
Tips for Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Creative composition is key to creating captivating aerial images and videos.
- Rule of Thirds: Position key elements along imaginary lines that divide the frame into thirds.
- Leading Lines: Use natural lines to guide the viewer’s eye through the scene.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Capture symmetrical scenes or repeating patterns for visual interest.
- Perspective: Use height to create unique perspectives and emphasize scale.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition and preventing costly repairs. A proactive maintenance schedule extends the lifespan of your drone and ensures its reliable performance.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
A routine maintenance schedule should include:
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the drone body and propellers to remove dirt and debris.
- Inspection: Inspect all components for damage or wear and tear.
- Calibration: Calibrate the drone’s sensors periodically to maintain accurate flight performance.
- Firmware Updates: Keep the drone’s firmware updated to benefit from bug fixes and new features.
Safe Storage and Transportation
Proper storage and transportation protect the drone from damage and ensure its longevity.
- Storage Case: Use a protective case to safeguard the drone during storage and transportation.
- Environmental Protection: Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from extreme temperatures.
- Secure Transport: Securely fasten the drone during transportation to prevent movement and damage.
Common Drone Problems and Causes
Understanding common drone problems and their causes enables quicker troubleshooting and resolution.
- Battery Issues: Low battery, faulty battery, improper charging.
- Connectivity Problems: Weak signal, interference, faulty receiver.
- Motor Malfunctions: Motor damage, loose connections, ESC issues.
- GPS Problems: Weak signal, obstructions, GPS module malfunction.
Effective Troubleshooting Techniques
Effective troubleshooting involves systematic checks and testing to pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Battery Issues: Check battery voltage, try a different battery, check charging system.
- Connectivity Problems: Check signal strength, move to an open area, check antenna connections.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motors, check connections, replace faulty parts.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to all applicable laws and regulations. Failure to comply can result in fines, legal action, and potential harm to others. Always check the specific regulations for your area.
Relevant Regulations and Laws
Drone regulations vary by country and region. Before flying, research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your area. This may include restrictions on flight zones, altitude limits, and required permits.
Best Practices for Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation involves prioritizing safety and respecting others’ privacy and property.
- Fly within visual line of sight.
- Respect airspace restrictions.
- Obtain necessary permits and licenses.
- Avoid flying near airports or other sensitive areas.
- Respect privacy and avoid filming people without their consent.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits and licenses before operating a drone. This process usually involves registering your drone and obtaining the necessary authorization for commercial or specific types of flights.
Steps Involved in Obtaining Permissions for Drone Flights
The process for obtaining permissions varies depending on location and regulations. Generally, it involves submitting an application, providing relevant information about the flight, and receiving approval before flying.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Beyond basic operation, advanced techniques enhance creative possibilities and expand the capabilities of your drone. Mastering these techniques allows for more dynamic and visually appealing aerial shots.
Achieving Specific Camera Angles and Shots
Advanced techniques allow for precise control over camera angles and movement, creating cinematic and visually compelling shots.
- Cinematic Shots: Utilizing smooth, deliberate movements to create visually appealing footage.
- Tracking Shots: Following a subject smoothly while maintaining a consistent distance and angle.
- Orbital Shots: Circling a subject to create a dynamic perspective.
Advanced Flight Modes
Advanced flight modes provide enhanced control and automation for complex flight maneuvers.
- Waypoint Navigation: Pre-programming a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously.
- Follow-Me Mode: The drone automatically follows a designated subject.
Comparing Different Drone Platforms and Capabilities
Different drone platforms offer varying capabilities in terms of camera quality, flight time, range, and features. Choosing the right platform depends on your specific needs and budget.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergency situations is critical for safe drone operation.
- Low-Battery Landings: Execute a safe landing procedure when the battery is low.
- Controlled Descents: Perform a controlled descent in case of malfunction or loss of control.
- Emergency Returns: Utilize the drone’s return-to-home function when necessary.
Illustrative Examples of Drone Operation: How To Operate A Drone
Real-world examples highlight the practical applications and potential challenges of drone operation.
Successful Drone Flight Scenario
A successful flight might involve pre-flight checks, a smooth takeoff and landing, and the capture of high-quality aerial footage of a landscape. The pilot maintains visual contact throughout the flight, adhering to all safety regulations and local laws. Post-flight, the drone is properly stored and maintained.
Drone Malfunction Scenario
A malfunction scenario could involve a sudden loss of GPS signal. The pilot, trained in emergency procedures, executes a controlled descent, lands the drone safely, and troubleshoots the GPS issue before resuming flight. The entire process emphasizes the importance of preparedness and quick thinking.
Complex Drone Flight Operation
A complex flight might involve a pre-planned flight path with multiple waypoints, utilizing advanced flight modes like waypoint navigation and follow-me mode to capture a complex series of shots. This demonstrates the integration of planning, technical skill, and understanding of drone capabilities.
Challenges and Rewards of Learning to Operate a Drone
Learning to operate a drone presents challenges, including mastering controls, understanding regulations, and troubleshooting technical issues. However, the rewards include the ability to capture stunning aerial footage, explore new perspectives, and potentially utilize drones for professional applications.
Successfully operating a drone involves a combination of careful planning, technical proficiency, and a strong commitment to safety. By mastering the pre-flight checklist, understanding drone controls, and adhering to all relevant regulations, you can unlock the immense potential of this versatile technology. Remember, responsible drone operation not only ensures your safety but also protects the airspace and environment. So, take to the skies with confidence, capture stunning visuals, and embrace the exciting possibilities that drone technology offers.
Happy flying!
Questions Often Asked
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and beginner modes are available. Research models known for their stability and ease of use.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which provides comprehensive guidance. From there, you can practice maneuvering and gradually increase the complexity of your flights, ensuring responsible drone operation at all times.
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced a significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses its GPS signal?
Immediately initiate a return-to-home function if available, or carefully maneuver the drone back to your location using visual cues. Land it safely as soon as possible.
How do I ensure my drone footage is legally compliant?
Always check and comply with local and national drone regulations, including airspace restrictions and privacy laws. Obtain necessary permits if required.
What’s the best way to clean my drone’s propellers?
Gently clean propellers with a soft brush and isopropyl alcohol to remove dirt and debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals.